
Anti Money Laundering Bitcoin Your Essential Compliance Guide
When your business accepts Bitcoin, you're stepping into the world of financial services, and that comes with a set of rules. Anti-money laundering (AML) compliance is simply the process you follow to prevent your business from being used for financial crime. It's about knowing your customers, watching out for strange transaction patterns, and reporting anything suspicious to the authorities.
Think of it as the security system for your financial operations.
Why You Can't Afford to Ignore Bitcoin AML Compliance

For a long time, crypto felt like the Wild West, a regulatory gray zone where businesses could operate with few hard-and-fast rules. Those days are long gone. Today, a solid AML program for your Bitcoin transactions isn't just good practice—it's a requirement for staying in business.
Regulators across the globe have moved from watching on the sidelines to actively enforcing the rules. Ignoring these obligations is a direct path to trouble. We're not just talking about fines; you could lose your banking partners, get locked out of important markets, and suffer reputational damage that's almost impossible to repair.
In this industry, trust is everything. A weak AML framework tells customers and partners you're a risk they can't afford.
Turn Compliance from a Headache into an Advantage
It's easy to see compliance as just another cost. I've seen many businesses make that mistake. The smart approach is to treat it as a strategic investment that actually helps you grow. When you build a transparent and robust compliance program, you're building trust.
Customers are savvier than ever about the risks of digital currencies, and they want to deal with businesses they know are secure and legitimate. This gives you a serious competitive edge.
Here’s how a proactive compliance mindset pays off:
- Strengthens Your Brand: Showing you’re serious about security and regulation builds a powerful reputation that attracts the right kind of customers.
- Keeps Your Banker Happy: Banks are much more open to working with crypto-friendly companies that can demonstrate strong AML controls. It makes their life easier, which makes your life easier.
- Prepares You for the Future: Regulations are only going to get stricter. With a solid framework in place now, you'll be ready to adapt without derailing your operations.
- Lowers Your Risk: By actively monitoring for trouble, you protect your business from accidentally getting involved in financial crime, keeping your assets and reputation safe.
The question isn't if you need an anti-money laundering policy for Bitcoin anymore. The real question is how you can make that policy work for you. The businesses that build compliance into the heart of their operations are the ones set up for long-term success.
What Regulators Are Watching
From FinCEN in the U.S. to the new MiCA regulations in Europe, regulators are getting on the same page about crypto. They are laser-focused on plugging the gaps that criminals love to exploit.
For example, they're paying close attention to CVC kiosks (crypto ATMs), which have seen a nearly 99% jump in fraud complaints. This tells you exactly where their priorities are.
The expectation is simple: if you accept Bitcoin, you need to know who you're dealing with and be confident their money is clean. This guide will walk you through the practical steps to build a compliance program that not only satisfies the regulators but makes your business stronger.
Crafting a Risk-Based AML Framework That Actually Works
When it comes to anti-money laundering for Bitcoin, a cookie-cutter approach is a recipe for disaster. The reality is, not all transactions carry the same risk. A risk-based approach is about being smart and focusing your compliance firepower where it’s needed most.
This isn’t just about satisfying regulators. It’s about creating a nimble, effective system that protects your business from financial crime without alienating your legitimate customers with unnecessary hurdles. The starting point is always a deep, honest look at your own business.
Pinpointing Your Unique Vulnerabilities
Every business has a unique risk fingerprint. A global e-commerce platform selling digital keys faces a completely different set of threats than a local coffee shop that accepts the occasional Bitcoin payment. To get a clear picture, you need to break down your operations.
Start by asking the right questions about your risk exposure:
- Customer Profile: Who are you dealing with? Individuals or businesses? Are they in countries with weak AML controls? Any user who is anonymous or pseudonymous automatically bumps up the risk level.
- Geographic Reach: The more borders you cross, the higher the risk. If your customer base is global, you’re not just dealing with one set of rules—you’re navigating a complex web of international regulations and sanctions lists.
- Products or Services: What are you selling? Digital goods are a classic money laundering vehicle because they’re delivered instantly and are difficult to trace back. Physical products shipped to a verified address are much lower on the risk scale.
- Transaction Patterns: Get familiar with what "normal" looks like for your business. You should be looking at the size, frequency, and timing of Bitcoin payments. A brand-new customer suddenly making a massive payment? That’s an immediate red flag.
Working through these factors systematically will show you exactly where you need to build up your defenses. For a more comprehensive look at building a solid foundation, exploring strategies for Mastering Regulatory Compliance Risk Management is a crucial next step.
Sorting Risks into Actionable Tiers
Once you’ve mapped out your potential weak spots, the next move is to categorize them. This is how you apply the right amount of scrutiny without slowing your business to a crawl. For most companies, a straightforward three-tiered system works best.
Here’s what that looks like in the real world:
- Low Risk: Think of a repeat customer you already know, buying a physical product and shipping it to a local address. For these, standard automated monitoring is perfectly fine.
- Medium Risk: Let’s say a new customer from another country signs up for a digital subscription. This transaction might trigger a request for basic ID verification before you give it the green light.
- High Risk: This is the big one. An unverified user from a high-risk jurisdiction trying to make a large, one-time purchase of an expensive digital item. This scenario demands everything you’ve got: enhanced due diligence, full identity verification, and a manual review by a trained analyst.
This tiered approach keeps your compliance efforts proportional to the threat. It stops you from putting every small, legitimate transaction through a painstaking process while ensuring the genuinely suspicious ones get the full-on investigation they require.
The goal of a risk-based framework is not to eliminate risk entirely—that's impossible. It's about understanding, managing, and mitigating your exposure in an intelligent and sustainable way.
The crypto crime scene is always evolving, which is why a rigid framework will fail you. For years, Bitcoin was the top choice for illicit activity, but the landscape has shifted. While Bitcoin's share of illicit transactions has fallen from 70% to just 20%, it's still a major player.
Sophisticated techniques like 'peel chains' are now used by 70% of crypto thieves to wash stolen funds, showing just how advanced your AML program needs to be. While stablecoins have now surpassed Bitcoin in illicit volume, the criminals' tactics are a threat to any business in the crypto space. You can get the full rundown on these trends in the CoinLedger 2025 Crypto Crime Report.
Mastering KYC And KYT For Bitcoin Payments
With your risk assessment mapped out, it’s time to build the engine of your anti money laundering Bitcoin program. This is where Know Your Customer (KYC) and Know Your Transaction (KYT) procedures come in. Far from being mere regulatory buzzwords, these two pillars are your active defense against illicit finance.
Think of KYC as the bouncer at your club. It’s the process you use to verify a customer's identity to make sure they're really who they say they are. For Bitcoin payments, this means you can't just operate on blind trust; you need a structured way to know who’s sending you money.
KYT, on the other hand, is like the network of security cameras watching every transaction. It taps into the public nature of the Bitcoin blockchain to analyze where the funds are coming from. The process screens incoming payments against huge databases of known illicit addresses, giving you a real-time risk score for every single transaction.
KYC vs KYT What Your Business Needs to Know
It's easy to get these two terms mixed up, but they serve distinct and complementary roles in a solid compliance strategy. KYC is about who your customer is, while KYT is about what their transaction history looks like.
| Aspect | KYC (Know Your Customer) | KYT (Know Your Transaction) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To verify a customer's identity and assess their individual risk profile. | To analyze the source of funds and the risk associated with a specific transaction. |
| Focus | Static customer data: name, address, ID documents. | Dynamic transaction data: wallet address history, source of funds, associated risks. |
| Timing | Primarily at onboarding, with periodic reviews. | Real-time, at the point of every single transaction. |
| Tools Used | ID verification software, document scanners, liveness checks, sanction list screening. | Blockchain analytics tools (Chainalysis, Elliptic), risk-scoring engines, on-chain monitoring platforms. |
Ultimately, you need both. Relying only on KYC means you could onboard a legitimate-looking customer who then uses illicit funds. Relying only on KYT means you might block a risky transaction but have no idea who the high-risk individual behind it was. They need to work together.
Implementing A Tiered KYC System
A one-size-fits-all approach to KYC is a recipe for disaster. It either creates too much friction for good customers or leaves massive security holes. The smart move is a tiered system that scales the level of identity verification based on the risk profile you’ve already established.
Here’s a practical way to structure it:
Tier 1: Basic Verification
For low-risk, small-value transactions (say, under $100), you might just ask for a name and a verified email. This keeps the checkout process fast and simple for most of your customers.Tier 2: Standard Verification
When a transaction crosses a higher threshold or involves a medium-risk element, you can step it up. Ask for a full name, physical address, and date of birth. This finds a good balance between security and user experience.Tier 3: Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
For high-risk activities—like unusually large payments or transactions from certain jurisdictions—you need to bring out the heavy-duty tools. This tier calls for a government-issued photo ID and maybe even a "liveness check" to confirm the customer is physically present.
This tiered method ensures your compliance efforts are proportional to the actual risk, making your anti money laundering Bitcoin strategy both effective and efficient. For a deeper dive into these concepts, check out our guide on the fundamentals of KYC in the crypto space.
Leveraging Blockchain Transparency With KYT
While Bitcoin can feel anonymous, its greatest strength for compliance is the blockchain itself—a public, unchangeable record of every transaction ever made. This transparency is pure gold for KYT.
KYT tools plug directly into the blockchain and use powerful analytics to trace the history of the Bitcoin being sent to your wallet. They cross-reference the source addresses with constantly updated lists of known bad actors, from sanctioned entities to darknet markets.
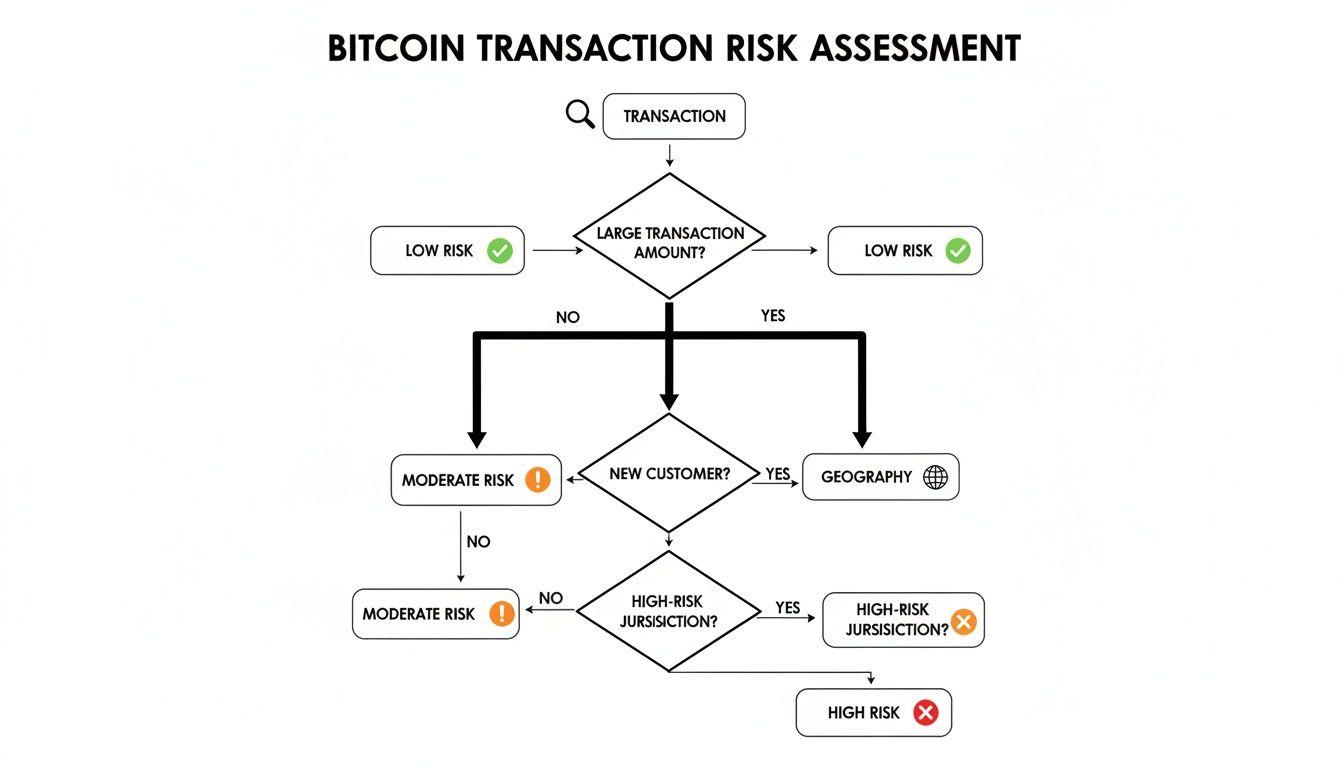
The key takeaway here is that a robust risk assessment isn't about one single data point. It’s about layering multiple signals—transactional, customer, and geographic—to get a clear picture of potential threats.
The power of KYT is its ability to flag suspicious funds before they settle in your account. It's the difference between preventing a problem and having to clean up a mess later.
Real-World KYT Scenarios
Let’s make this real. Imagine you run an e-commerce store. A new customer places a huge order and opts to pay with Bitcoin. Your integrated KYT service instantly flags the payment. Why? Because the Bitcoin originated from a wallet address directly linked to a known darknet marketplace. You can now halt the order before any goods are shipped.
Here’s another one: identifying payments from coin "mixers." These services are designed to obscure the trail of funds. While not always used for illicit purposes, they are a major red flag for money laundering. A good KYT tool will immediately alert you to transactions that have passed through a mixer, letting you pause the order for a closer look.
The need for these tools isn't theoretical. According to Chainalysis, North Korean hackers alone stole over $1 billion in cryptocurrency in 2022, washing the funds through complex chains of mixers and shadowy brokers. With regulators handing out massive AML fines, you can't afford to be caught off guard.
Setting Up Smart Transaction Monitoring and Reporting
Effective anti money laundering Bitcoin compliance isn't a "set it and forget it" task. Once you’ve onboarded a customer, the real work begins: watching their activity. This is where you build an automated system that acts as your vigilant watchdog, flagging suspicious behavior 24/7.

The foundation of this system is a set of clear rules and alerts tailored to the risks you identified earlier. You’re essentially teaching your system what "normal" looks like for your business so it can spot the outliers. It’s about moving beyond a simple KYC check and getting into the nitty-gritty of analyzing transaction behavior as it happens.
Defining Your Red Flag Rules
Your monitoring rules should be a direct reflection of your risk assessment. If you flagged cross-border payments as a medium risk, you absolutely need a rule to flag them. These rules aren't set in stone, either—they have to evolve as your business grows and as bad actors get more creative.
I recommend starting with these common red flags:
- Transaction Structuring: This is a classic money laundering technique. Someone breaks a large transaction into smaller chunks to fly under the radar. You can set an alert to trigger if a single customer makes multiple payments that, when added up, fall just under your reporting threshold within a short period.
- Geographic Hotspots: Flag every transaction coming from or going to wallets associated with high-risk jurisdictions or countries under international sanctions. This is non-negotiable.
- Interaction with Illicit Services: A good KYT provider will automatically flag any transaction with a direct or indirect link to darknet markets, mixing services, or known scam wallets.
- Unusual Velocity: Keep an eye out for a sudden spike in the frequency or value of transactions from an account that has been relatively quiet. That change in behavior is often a major tell.
Think of these rules as an automated first line of defense. They allow your team to stop chasing ghosts and focus their energy on the transactions that genuinely warrant a closer look. Managing these alerts is a core part of any strong compliance program. You can dive deeper into the mechanics in our guide on crypto transaction tracking.
An alert doesn't automatically mean a transaction is illicit. It's simply a signal that something is outside the norm and requires human review. The goal is to investigate, document, and decide on the next steps with confidence.
From Alert to Action: A Clear Investigation Path
When an alert fires, panic is your worst enemy. A clear, documented process is crucial for staying organized and effective. Your team needs a standard operating procedure (SOP) that outlines exactly what to do next.
A typical investigation workflow I’ve seen work well looks like this:
- Initial Triage: A compliance analyst gives the alert a quick review. Is it obviously a false positive, or does it need a deeper dive?
- Data Gathering: The analyst pulls together all the relevant info—the customer's KYC data, their transaction history, and the specific reason the KYT tool flagged the payment.
- Analysis: Now, the analyst looks at the complete picture. For instance, a large payment might seem suspicious on its own, but if it comes from a long-standing, verified corporate client, it's likely legitimate business. Context is everything.
- Decision and Documentation: Based on the evidence, the analyst decides whether to approve the transaction, request more information from the customer, or escalate it for potential reporting. Every single step and decision must be meticulously documented.
More and more, Machine Learning Fraud Detection is becoming a game-changer for smart transaction monitoring and beefing up AML defenses.
Demystifying Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs)
If an investigation concludes that a transaction is, in fact, suspicious, you have a legal obligation to file a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with the relevant financial intelligence unit (like FinCEN in the United States). This step can feel intimidating, but it’s a straightforward process if you’ve done your homework.
A SAR isn't an accusation; it's a formal heads-up that you've observed activity that could be related to financial crime. The key is to be factual, detailed, and clear. Your report should cover the who, what, when, where, and why you believe the activity is suspicious, backed up by all the documentation you gathered during your investigation.
Make no mistake, the regulatory environment is getting tougher. 2025 was a record-breaking year for AML enforcement in the crypto world, with entities facing over $1 billion in penalties. That figure alone highlights the severe consequences of getting this wrong and underscores the urgent need for robust, real-time monitoring systems. This regulatory pressure is precisely why a well-oiled monitoring and reporting machine is no longer a nice-to-have—it's a core business necessity.
Weaving AML Tools into Your Payment Gateway
Alright, so you’ve got a solid AML framework on paper. The next, and arguably most important, step is making it a living, breathing part of your daily operations. This is where your payment gateway stops being just a tool for getting paid and becomes your first line of defense.
The whole point is to embed your anti money laundering Bitcoin checks directly into the payment flow. When done right, these checks happen automatically, in the background, without creating a clunky or suspicious checkout experience for your legitimate customers.
Modern payment gateways are built for this. Many, like BlockBee, either come with their own compliance features or offer simple API connections to top-tier Know Your Transaction (KYT) service providers. This integration is what lets you shift from a reactive, after-the-fact compliance stance to a proactive one.
Instead of a person manually reviewing transactions hours or days later, the system does the work instantly. A customer pays with Bitcoin, your gateway pings a KYT service with the transaction details, gets a risk score back, and makes an automated decision based on your rules—all of this happens in the blink of an eye.
Choosing Your Integration Path
When it comes to integrating AML tools, you're generally looking at two main routes. The best one for you really boils down to your technical team's capacity and your specific business needs.
- Native Gateway Integrations: This is the plug-and-play option. Some payment gateways have compliance tools built right in, which means less setup and a single dashboard to manage everything. It's a fantastic choice if you want a powerful solution without tying up your developers.
- API-Based Connections: If you have more unique requirements or want to hand-pick your analytics provider, connecting via an API gives you total control. This path lets you select the exact KYT tool that matches your risk appetite and weave it deeply into your existing tech stack.
For a closer look at how these connections are built, it’s worth exploring a solid crypto payment gateway API to understand the mechanics of creating these kinds of custom, automated workflows.
Putting It on Autopilot with Webhooks
Let's get practical. One of the most elegant ways to automate this entire process is with webhooks. Think of a webhook as an automated message that one application sends to another when something specific happens. In our case, that "something" is a new Bitcoin payment.
Here’s how it plays out: a customer buys something from your store. The second your payment gateway confirms the transaction, it fires off a webhook. This webhook instantly sends key data, like the transaction ID and wallet address, to your connected KYT service. The KYT service then does its job, analyzing the transaction's history and sending back a risk score.
By using webhooks and a programmable payment flow, you can build a completely automated AML system. If a transaction comes back with a high risk score, the system can instantly flag the order for a human to review or even cancel it automatically. This protects your business 24/7, no manual intervention needed.
The best part? This entire sequence happens behind the scenes in seconds. Your customer gets a smooth checkout, totally oblivious to the sophisticated security checks happening to protect both them and your business.
A Real-World Code Example
To give you a better idea of how this looks in practice, here's a simplified code snippet. This is a basic server-side script that listens for a payment webhook and then triggers a KYT check.
// This is a simplified example for illustrative purposes.
// It uses Express.js for the server.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const kytProvider = require('your-kyt-provider'); // Your chosen KYT service
app.post('/payment-webhook', async (req, res) => {
const { transactionId, sourceAddress } = req.body;
// Trigger a real-time KYT check
const riskScore = await kytProvider.getRiskScore(sourceAddress);
if (riskScore > 75) {
// High-risk transaction detected
console.log(High risk for TXID ${transactionId}. Flagging for review.);
// Add logic here to place the order on hold
} else {
// Low risk, proceed with the order
console.log(Low risk for TXID ${transactionId}. Processing order.);
// Add logic here to fulfill the order
}
res.status(200).send('Webhook processed.');
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Listening for webhooks...'));
This simple script shows the core logic: receive payment data, check the risk, and act on your pre-set rules. This level of automation isn't just a nice-to-have anymore; it's a critical piece of any effective anti money laundering Bitcoin strategy.
Putting It All Together: Your Bitcoin AML Compliance Checklist
Alright, let's move from the "what" to the "how." Building a solid anti money laundering Bitcoin framework isn't a set-it-and-forget-it task; it’s a living process. This checklist breaks down the essentials into practical, actionable steps to get your program off the ground and keep it running smoothly.
Think of this as your roadmap. Every business is different, so you'll need to tweak these points to match your own risk appetite, customer base, and the scale of your operations. The goal here is consistency and diligence.
Core Compliance Actions
Conduct and Document a Real-World Risk Assessment: Start by mapping out your actual vulnerabilities. Where do your customers come from? What products or services are they buying with Bitcoin? This documented assessment is the cornerstone of your entire compliance strategy.
Appoint a Compliance Officer: Someone needs to own this process. Even if you're a small team, designate one person to be the go-to for overseeing the AML program, keeping up with regulatory shifts, and making the final call on tricky situations.
Develop a Written AML Policy: Get your procedures down on paper. This formal document should clearly explain how you handle customer verification (KYC), transaction monitoring, reporting, and record-keeping. It's not just a formality for regulators—it's your team's playbook.
Implement Tiered KYC Procedures: Don't treat every customer the same. Create a risk-based system for verification. For example, a small, one-time purchase might require minimal info, while larger or recurring transactions trigger more in-depth checks. This keeps the process efficient and reduces friction for legitimate, low-risk users.
Ongoing Monitoring and Tooling
A policy document is only as good as its execution. Effective compliance is all about staying vigilant, which means having the right processes and technology to watch over transactions and act quickly when something looks off.
Integrate a KYT Solution: This is non-negotiable. Your payment system must be connected to a reputable blockchain analytics tool. This will automatically screen every single incoming Bitcoin transaction against databases of known illicit addresses before you even process the payment.
Define Your Monitoring Rules and Alerts: What does "suspicious" actually look like for your business? Set up automated alerts for specific red flags, such as multiple small payments that seem designed to fly under the radar (structuring), funds coming from high-risk countries, or transactions linked to tumblers or mixers.
Establish a Clear SAR Filing Protocol: When an alert fires, what happens next? Create a simple internal workflow for investigating suspicious activity and, when your investigation confirms a problem, a clear process for filing a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with the proper authorities.
Train Your Team Regularly: Everyone who touches a Bitcoin payment needs to understand the basics. Make sure your team knows what your AML policy says, can spot common red flags, and knows exactly who to tell when they see something concerning.
Common Questions About Bitcoin AML
Stepping into the world of Bitcoin anti-money laundering compliance always brings up questions. As you start accepting crypto, you'll run into specific scenarios that don't always have textbook answers. Let's tackle some of the most frequent questions I hear from business owners and developers.
The idea here is to give you clear, practical answers without drowning you in legal speak. Consider this your go-to guide for those tricky gray areas.
Does My Small Business Really Need an AML Program?
In most cases, yes—if your business is classified as a Money Services Business (MSB). In the United States, for example, FinCEN has been clear that businesses accepting and transmitting virtual currencies like Bitcoin usually fit this description.
It’s a huge misconception that AML rules are only for big banks. The regulations target the activity, not the size of your company. That means even a small e-commerce shop taking Bitcoin could need to register as an MSB and build out a formal AML program. It all comes down to how your business model lines up with the regulatory definitions where you operate.
What’s the Difference Between a Mixer and a Chain Hopper?
Both are ways to muddy the waters and hide where funds came from, but they work quite differently. Knowing the difference is key to spotting red flags in your transaction monitoring.
- Mixers (or Tumblers): Think of these as a big pot. A mixer service throws transactions from tons of users into this pot and then sends the mixed-up funds back out. The goal is to snap the on-chain link between the Bitcoin someone sent and what they received, making it a nightmare to trace.
- Chain Hopping: This is a bit more sophisticated. It's the practice of moving funds from one blockchain to another using cross-chain bridges. For instance, someone could swap stolen Bitcoin for a privacy coin like Monero on a different network, then trade it back to something like a stablecoin. They're essentially laundering the funds across multiple ledgers.
While mixers are a classic red flag, chain hopping has become incredibly common. Your Know-Your-Transaction (KYT) tools have to be sharp enough to see when funds have jumped between blockchains, or you’ll miss a massive part of the risk picture.
How Long Do I Have to Keep AML Records?
Record-keeping isn't just a suggestion; it's a pillar of compliance. In the U.S., the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) requires financial institutions—and that includes crypto MSBs—to hold onto most records for at least five years.
And we're not just talking about a list of transactions. This five-year rule applies to a whole range of documents:
- All the KYC information you gathered when a customer signed up.
- Your internal risk assessment documents and the AML policy itself.
- Notes and findings from any suspicious activity investigations you conducted.
- Copies of any Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) you've filed.
Hanging onto these records properly means you're ready for any regulatory audits and can prove you’ve been compliant all along. It’s the paper trail that shows you’re taking your Bitcoin anti-money laundering duties seriously.
Ready to build a secure and compliant payment system? BlockBee provides the tools you need to accept crypto payments with confidence. Our non-custodial gateway and easy API integrations make implementing your AML strategy straightforward.
