
What is bitcoin address: How it works and why it matters
A Bitcoin address is a unique string of letters and numbers that essentially acts as a digital mailbox for your crypto. The easiest way to think about it is like an email address, but for money. It's a public destination where anyone can send you Bitcoin, but only you, with your private key, can open it and access the funds inside.
Your Digital Mailbox on the Blockchain
At its heart, a Bitcoin address is simply a destination on the blockchain network. Just like a bank account number tells a sender where to send a wire transfer, a Bitcoin address gives them a specific location to direct a transaction. The key difference is that a Bitcoin address isn't tied to your real-world identity, which gives you a level of pseudonymity.
This public identifier is mathematically derived from your wallet's public key, which in turn is generated from a secret private key. It's perfectly safe to share your Bitcoin address with anyone, but your private key must be kept secret at all costs. That key is the only thing that proves ownership and allows you to spend the Bitcoin sent to your address. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on the differences between a crypto wallet and an address.
The Role of an Address in Transactions
Whenever you want to receive Bitcoin, you just need to give the sender one of your addresses. This alphanumeric string, which is usually between 26 and 35 characters long, makes sure the funds land in your wallet. Once the transaction is sent to the network and confirmed, the Bitcoin is officially yours.
To make this crystal clear, let's compare it to something we all know: traditional banking.
Bitcoin Address Analogy Breakdown
This table breaks down how the key parts of a Bitcoin transaction stack up against a familiar bank transfer.
| Concept | Bitcoin Analogy | Traditional Banking Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Destination | Bitcoin Address | Bank Account Number |
| Access Key | Private Key | PIN or Password |
| Public Ledger | Blockchain | Bank's Private Ledger |
As you can see, the concepts are quite similar, but Bitcoin's approach offers a more open and decentralized model.
The use of these addresses is a fantastic way to measure network activity. For example, during the market frenzy in April 2021, the daily number of unique, active Bitcoin addresses shot up to nearly 1.1 million in a single day. This surge shows just how many transactions were flying across the network, and it all hinges on the simple, yet powerful, role of the Bitcoin address. Without them, the entire system of sending and receiving value couldn't exist.
How Your Bitcoin Wallet Creates an Address
A Bitcoin address doesn't just appear out of thin air. It’s the final piece of a brilliant cryptographic puzzle, all starting with one thing your wallet creates the moment you set it up: a private key.
Think of your private key as the master key to a digital vault. It’s a massive, randomly generated number that holds the ultimate power over your funds. Anyone who gets their hands on it has complete control, which is why you must guard it obsessively. Everything else your wallet does flows from this single secret.
From that private key, your wallet uses some clever one-way math to generate a corresponding public key. The relationship is like a unique lock and key. The private key is the only thing that can open the lock (the public key). You can share the public key freely because it's mathematically impossible for someone to work backwards and figure out your private key just by looking at the lock.
The Journey from Key to Address
So where does the actual address come from? The string of characters you share with others is a compressed, user-friendly version of your public key. It even has a built-in checksum, which is a fancy way of saying it has error-detection. This little feature is a lifesaver, as it prevents a simple typo from sending your funds into a digital black hole.
This image helps bridge the gap between how we think about traditional banking and how a Bitcoin transaction actually works.
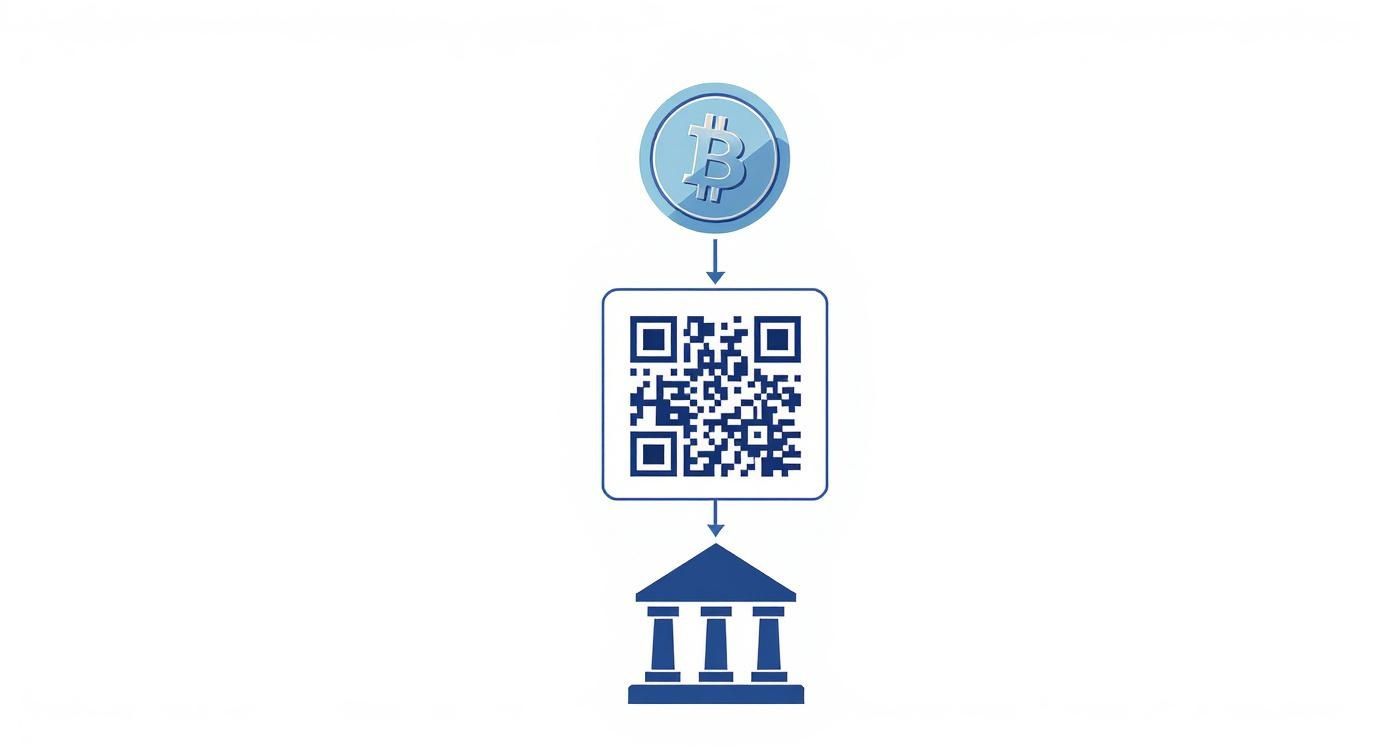
As you can see, the address acts as the destination—the account number, so to speak—linking the decentralized world of Bitcoin to a concept we can all understand.
Modern Wallets and Seed Phrases
Back in the early days, managing private keys was a nightmare. Lose the key, and your bitcoin was gone forever. Thankfully, modern wallets have evolved, and most now use a system called Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets.
When you first set up an HD wallet, it generates a single "master seed." You'll recognize this as your 12 or 24-word recovery phrase. This phrase is the ultimate backup for your entire wallet.
Key Takeaway: That 12 or 24-word seed phrase is the master key to everything. From that one phrase, your wallet can mathematically regenerate every single private key, public key, and Bitcoin address you've ever used or will ever use.
This structure is a game-changer for a few reasons:
- Simple Backup: You only have one thing to write down and secure—that recovery phrase. It backs up all past, present, and future funds.
- Enhanced Privacy: Your wallet can spit out a brand-new address for every transaction. This makes it incredibly difficult for anyone to connect the dots and track your financial history.
- Better Organization: It allows for sophisticated account structures, which is a huge plus for businesses that need to separate different income streams.
The software engineering that makes this all possible is seriously impressive. If you're curious about what goes into building these systems, looking at technical lead roles in crypto wallet development gives you a sense of the expertise required. Thanks to HD wallets, we get to enjoy Fort Knox-level security without needing to be cryptography experts ourselves.
What Are All These Different Bitcoin Address Formats?
When you first dive into Bitcoin, you’ll notice addresses don't all look the same. Some start with a 1, others with a 3, and the newest ones begin with bc1. This isn't just a random quirk; each format is a deliberate upgrade, designed to make the Bitcoin network better over time.
Think of it like the evolution of phone numbers. We started with local numbers, then added area codes for long-distance, and eventually country codes for international calls. Each addition solved a new problem. Bitcoin addresses evolved in a similar way, with each new format offering lower fees, better security, or new features.
Knowing the difference isn't just trivia—it has a direct impact on how much you pay in transaction fees and which wallets or exchanges you can use. Let's break down the three main types you'll run into.
The Originals: Legacy Addresses
The very first Bitcoin address format is what we now call Legacy or P2PKH (Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash). You can spot these instantly because they always start with the number '1'.
For a long time, this was the only kind of address there was. It did its job, but as Bitcoin grew, its limitations started to show. Transactions coming from Legacy addresses are bigger in terms of data size. Since Bitcoin fees are based on how much data your transaction takes up on the blockchain (not the amount you're sending), this makes '1' addresses the most expensive to use.
While they have the advantage of being compatible with literally every Bitcoin wallet and service ever created, their higher fees mean they’ve fallen out of favor. Most modern wallets still let you send to a Legacy address, but they won’t generate one for you by default anymore.
The Bridge to the Future: P2SH Addresses
Next up are addresses that start with the number '3'. These are called P2SH (Pay-to-Script-Hash) addresses. They were a really clever development that served as a bridge to more advanced features without forcing the entire network to upgrade at once.
P2SH addresses are best known for enabling two major innovations:
- Multi-Signature Security: They made it much easier to create wallets that require signatures from multiple people (or devices) to approve a transaction. This was a huge leap forward for securing company funds or joint accounts.
- SegWit Compatibility: They also provided a backward-compatible on-ramp for Segregated Witness (SegWit), a critical network upgrade aimed at lowering fees and helping the network handle more transactions.
Sending from a '3' address is significantly cheaper than from a Legacy one, typically saving you around 25-35% on fees. Thanks to their mix of lower fees and wide compatibility, they became the dominant address type for years and are still very common today.
The Modern Standard: Bech32 (Native SegWit)
The latest and greatest format is Bech32, often called Native SegWit. These are the easiest to recognize because they always start with 'bc1'.
Bech32 addresses are the direct result of the SegWit upgrade and were built from the ground up for maximum efficiency. They offer the lowest possible transaction fees—often 50-60% cheaper than Legacy addresses. They also come with some great design improvements.
A Clever Design Choice: Bech32 addresses are not case-sensitive (they're always lowercase) and have a stronger error-detection system built in. This makes them much harder to mistype, drastically reducing the chances of sending your Bitcoin into the void because of a simple typo.
The only real hurdle for Bech32 was adoption. For a while after they were introduced, not all wallets and exchanges supported sending to a 'bc1' address. Thankfully, that's almost entirely a problem of the past. Today, Bech32 is the gold standard for anyone who wants to save money on fees and use Bitcoin's most advanced tech.
To make it easier to tell them apart at a glance, here’s a quick rundown of the key differences.
Comparison of Bitcoin Address Formats
| Format Type | Starts With | Key Benefit | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy (P2PKH) | 1 |
Universally supported by all wallets and services. | Highest transaction fees. |
| P2SH (SegWit Compatible) | 3 |
Balances lower fees with wide compatibility. | Excellent; supported almost everywhere. |
| Bech32 (Native SegWit) | bc1 |
Offers the lowest possible transaction fees. | High; now the modern standard. |
At the end of the day, understanding these formats is a core part of truly understanding what a Bitcoin address is. Being able to recognize them helps you make smarter choices, minimize fees, and troubleshoot any issues that might come up.
Best Practices for Address Security and Privacy
Knowing what a Bitcoin address is and how it functions is a great start, but it's only half the story. The real challenge is using them safely to protect your assets and maintain your financial privacy. It’s easy to forget that the Bitcoin blockchain is a public bookkeeper—every single transaction is out there for anyone to see. This level of transparency means you have to be disciplined.
Why You Should Never Reuse Addresses
If there's one habit you need to build, it's this: use a new Bitcoin address for every single transaction you receive. This is the golden rule of Bitcoin hygiene.
When you reuse an address, you're creating a public breadcrumb trail. Anyone curious enough can follow that trail, connecting all your incoming and outgoing payments. Before you know it, they've pieced together a surprisingly detailed picture of your financial life.
Thankfully, modern Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets make this incredibly simple. They can generate a seemingly infinite number of new addresses from your one master recovery phrase. So, there’s really no extra work involved. Just tap "receive," and your wallet serves up a fresh, unused address, every time.

A Little Privacy Goes a Long Way
A Bitcoin address isn't truly anonymous; it's pseudonymous. Since all transaction histories and balances are traceable on the blockchain, privacy is something you have to actively maintain. This transparency is key to how the network works, but it comes with trade-offs.
Firms specializing in on-chain analysis can track global usage patterns, which helps estimate the network's health—some estimates place the number of active users somewhere between 30 to 60 million a month.
Reusing an address makes it laughably easy for observers to cluster all your activity. Imagine receiving your salary, buying a coffee, and donating to a political cause all from the same address. Anyone can connect those dots. By generating a new address for each payment, you break that chain of association, making your financial history much harder for outsiders to piece together.
The Verification Habit That Can Save You a Fortune
Bitcoin transactions are final. There's no "undo" button, no customer support to call if you make a mistake. Once you hit send, those funds are gone forever. This unforgiving reality makes careful verification an absolutely critical step.
One of the most devastating and common mistakes is sending bitcoin to the wrong address. Scammers know this and have cooked up some clever ways to exploit a moment of carelessness. One of the nastiest tricks is the "address poisoning" attack.
Here's how it works: An attacker sends a tiny "dust" transaction to your wallet. The trick is, they send it from an address they created to look almost identical to one you've used before—it shares the same first and last few characters. Later, when you're looking through your transaction history to send funds, you might accidentally copy their lookalike address instead of the legitimate one.
To avoid this nightmare scenario, you have to get into the habit of verifying the entire address, not just glancing at the beginning and end.
Here are a few tips to build into your routine:
- Triple-Check Before You Send: Seriously, read the whole address out loud. Compare it character-by-character against the original. A few seconds of friction can prevent a world of hurt.
- Use QR Codes Whenever Possible: Scanning a QR code is way less error-prone than manually copying and pasting that long jumble of characters.
- Watch Out for Clipboard Malware: Some nasty malware sits in the background, watching your clipboard. When it detects a Bitcoin address, it instantly swaps it with the attacker's. The fix? Always paste the address, then check it one last time against the source before you confirm.
Securing the Source of Your Addresses
At the end of the day, the security of your Bitcoin addresses comes down to one thing: the security of the private keys that control them. The address itself can't be "hacked," but the private key that unlocks the funds certainly can be.
Protecting your wallet's recovery phrase is your most important job. Never, ever store it digitally—not on your computer, not in your email, and definitely not in a cloud drive. Write it down on paper (or better yet, stamp it into metal) and hide it somewhere safe. For a deeper dive, it's worth brushing up on the fundamentals of private key security to make sure your foundation is rock-solid.
How Businesses Handle Bitcoin Address Payments
If you’re just one person managing a personal Bitcoin wallet, handling an address is simple enough. But for a business? Trying to manually create, track, and balance payments coming into a single, static address is a recipe for disaster. It’s an accounting nightmare, it puts customer privacy at risk, and it practically invites payment mix-ups.
To run things smoothly, businesses need to think of a Bitcoin address not as a permanent mailbox, but as a dynamic, single-use tool for every transaction. This is where payment gateways enter the picture. Instead of just slapping a BTC address on their website, savvy businesses use specialized platforms to manage crypto payments from start to finish.

Automated Address Generation for Invoices
At the heart of any modern crypto payment system is its ability to generate a unique Bitcoin address for every single invoice. When a customer heads to checkout and chooses to pay with Bitcoin, the gateway’s API instantly creates a brand-new address tied only to that specific order.
This one-to-one mapping between an address and an invoice is a total game-changer. It solves the biggest headache of manual processing overnight: trying to figure out who paid what. Since each payment lands in a unique spot, the system knows exactly which order to mark as complete. No guesswork required.
Key Takeaway: Never reusing addresses doesn't just make accounting easier; it dramatically improves customer privacy. This approach prevents snoops on the blockchain from connecting a customer's payment back to your main business wallet, keeping their financial activity private.
This automated system delivers some serious benefits:
- Payment Certainty: You’ll never have to wonder which customer sent that 0.0015 BTC when three different orders had the same total.
- Enhanced Privacy: It keeps both your business's and your customers' transaction histories from being easily linked on the public ledger.
- Accurate Tracking: Reconciling payments becomes a breeze because every incoming transaction is already matched to a specific sale.
Creating a Seamless Checkout Experience
A clunky payment process kills conversions. Crypto payment gateways make the checkout flow completely intuitive by giving the customer everything they need on one screen. This usually means a QR code that bundles both the unique Bitcoin address and the exact payment amount.
Customers just scan the code with their mobile wallet, and both the destination address and the BTC amount are filled in automatically. This simple step wipes out the risk of copy-paste mistakes or accidental underpayments—common friction points that lead to abandoned carts and frustrated support tickets. If you want to dive into the technical side, exploring a crypto payment gateway API shows you the backend magic that makes this happen.
And it's not just about Bitcoin anymore. The same concept of smooth, address-based payments is spreading. For instance, more e-commerce sites are looking into integrating other cryptocurrency payment methods like Solana Pay, applying these same principles to other digital assets.
Managing Payouts at Scale
The need for automation doesn't stop at receiving money. What if you’re running an affiliate program, a freelance marketplace, or a gaming platform? You might need to send payments to hundreds, or even thousands, of people. Doing that by hand is not just slow—it's practically guaranteed to lead to expensive mistakes.
This is exactly what mass payout tools were built for. Platforms like BlockBee let businesses upload a single file with a list of recipient addresses and the amounts they're owed. With one click, the system handles the entire disbursement, sending out all the payments in an efficient batch. This saves countless hours, slashes the risk of human error, and ensures your partners get paid correctly and on time, all while you maintain full, self-custodial control over your company’s funds.
Watch Out for These Common Mistakes and Address Scams
One thing about Bitcoin is that transactions are final. There’s no "undo" button. This means a tiny slip-up can lead to your funds being gone for good. Staying safe is all about knowing what to look for—both the simple mistakes and the clever scams people cook up. A little bit of caution and a careful process for every transaction is your best defense.
A surprisingly common and painful error is sending crypto to an address on the wrong blockchain. Think sending Bitcoin (BTC) to a Bitcoin Cash (BCH) address. They sound similar, but they're entirely different networks, and a mistake like that can easily result in a permanent loss. Most modern wallets have built-in checks to stop this, but it’s a great reminder to always, always double-check you’re on the right network.
Spotting Sophisticated Address Scams
Scammers are always getting more creative. One of the sneakiest tricks out there today is the "address poisoning" attack. It’s designed to prey on the habit of copying addresses from your transaction history.
Here’s how they pull it off:
- The Lookalike: A scammer creates a wallet address that looks almost exactly like one you’ve used before. They use special software to generate a "vanity" address where the first and last few characters are a perfect match.
- The "Poison": They send a minuscule amount of crypto—sometimes called "dust"—from their lookalike address to you. This transaction now appears in your wallet’s history, planting the trap.
- The Bait: The next time you need to send money, you might glance at your transaction history and copy what you think is the right address. If you only check the beginning and end, you could easily grab the scammer’s address by mistake.
Once you hit send, your funds go straight to the attacker. There’s no getting them back. Studies have shown that thousands of these poisoning transactions are happening, with scammers willing to spend a little on transaction fees for the chance at a big payday from a single mistake.
Building Your Defensive Habits
Your best protection is to build a solid, consistent routine. You can't call up a bank and ask for a chargeback, so the responsibility for getting it right is all on you.
The Golden Rule of Sending Crypto: Always verify the entire address, character by character, before you confirm a transaction. Never trust just the first and last few characters—that’s the exact vulnerability address poisoning scams are built to exploit.
Here are a few practical habits that will keep your crypto safe:
- Use QR Codes: Whenever you have the option, scan a QR code instead of copying and pasting an address. It's faster and almost completely eliminates the risk of typos or other copy-paste errors.
- Watch for Clipboard Malware: There’s a nasty type of malware that quietly watches your clipboard. The moment you copy a Bitcoin address, it swaps it with the scammer’s address. Give the pasted address in your wallet one final, careful check before sending.
- Use an Address Book: If you’re sending funds to the same person or business regularly, save their address in your wallet's address book. This creates a trusted, pre-verified contact, so you never have to copy and paste their address again.
Your Bitcoin Address Questions, Answered
Getting comfortable with Bitcoin means getting answers to the practical questions that pop up along the way. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to clear up how Bitcoin addresses work and how you can use them with confidence.
Can a Bitcoin Address Be Tracked?
Yes and no. Every single transaction tied to a Bitcoin address is etched onto the public blockchain forever. That means anyone with an internet connection can look up an address and see its complete history—every payment in, every payment out, and the current balance.
But here's the catch: the address itself is pseudonymous. It's just a string of characters, not your name and home address. It only gets linked to your real-world identity if you tie it to a regulated exchange (which requires ID) or publicly announce you own it. This is precisely why using a fresh address for every transaction is the gold standard for privacy.
How Many Bitcoin Addresses Can I Have?
As many as you want. Seriously—the number is virtually infinite. Modern wallets, often called Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets, can generate billions of unique addresses from a single master "seed," which is your 12 or 24-word recovery phrase.
This isn't just a neat trick; it's a cornerstone of good privacy. Since creating new addresses costs nothing and has no limits, you should make it a habit to generate a new one for every single payment you receive.
A Crucial Point: While you can have an endless supply of addresses, they all trace back to that one recovery phrase. Guarding that phrase is everything. It's the master key to all your funds, across all your addresses.
What Happens if I Lose Access to My Address?
Let's be precise here: you don't really "lose an address." You lose the private key that controls it. If you lose the private key—or the recovery phrase that generates it—any Bitcoin held at that address is gone for good. There’s no "forgot password" link, no support line to call. The funds are locked away, permanently out of reach.
This is the harsh, unforgiving side of self-custody, and it highlights just how critical it is to back up your wallet's recovery phrase somewhere incredibly safe.
Is It Safe to Share My Bitcoin Address?
Absolutely. Sharing your Bitcoin address is not only safe, it's necessary. It's how people send you bitcoin. Think of it like your bank account number or your email address—it's the public-facing information someone needs to send you something.
The one thing you must never, ever share is your private key or your 12/24-word recovery phrase. That’s the secret key to the vault. Sharing it is like handing over your signed, blank checks.
The use of these addresses is exploding. Globally, the number of crypto users has blown past 560 million, and adoption has skyrocketed over 18,600% in just a few years. This shows just how fundamental these addresses have become. You can dig into the numbers and see how Bitcoin adoption is shaping global finance.
Juggling countless addresses for your business sounds like a headache, right? BlockBee takes care of it for you. Our platform automatically creates a unique address for every single invoice, which keeps your books clean and protects your customers' privacy. Check out our secure, non-custodial payment solution at https://blockbee.io.
