
Your Ultimate Guide to Gas Fee Crypto and How It Works
Think of a crypto gas fee as the toll you pay to drive on a blockchain highway. Every time you do something on the network—whether it's sending coins to a friend or minting an NFT—you're using the network's processing power. The gas fee is simply the payment you make to the validators who put their computers to work to make it all happen, keeping the blockchain secure and running smoothly.
What Is a Gas Fee and Why Does It Matter?

At its heart, a gas fee is a transaction cost. It’s not so different from the small percentage fee a credit card company charges a merchant for processing a sale. On a blockchain, this fee serves a critical purpose: it stops spammers from flooding the network with junk transactions and helps allocate the blockchain’s finite resources to users who genuinely need them.
For any business that accepts cryptocurrency, getting a handle on these fees is non-negotiable. It directly impacts your profit margins and can make or break the customer's checkout experience.
Let's stick with the highway analogy. Imagine the Ethereum network is a major city with a fixed number of roads. During rush hour, traffic backs up, and drivers in a hurry might be willing to pay more for an express lane. Gas fees behave in the exact same way. When the network is swamped with transactions, the price to get your transaction processed quickly shoots up.
The Core Components of a Gas Fee
To really understand how gas fees are calculated, you just need to know three key terms. They sound a bit technical, but the ideas behind them are surprisingly simple.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the essential terms you'll encounter when dealing with gas fees, especially on networks that have adopted Ethereum's EIP-1559 model.
Key Gas Fee Components at a Glance
| Term | Simple Analogy | What It Really Means |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Limit | The maximum gallons of fuel your car can use for a trip. | The maximum amount of computational work (gas) you're willing to pay for on a single transaction. A simple transfer needs less gas than a complex smart contract. |
| Base Fee | The standard, non-negotiable toll for using the highway. | This is the minimum price-per-unit-of-gas required for your transaction to be considered for inclusion in a block. The network automatically adjusts this fee up or down based on how busy it is. |
| Priority Fee (Tip) | An extra tip you give the toll booth operator to let you cut the line. | An optional amount you can add to your transaction to incentivize validators to process it faster. During busy times, a higher tip can make all the difference. |
So, you have the gas limit, the base fee, and the optional priority fee. These three components work together to determine the final cost of your transaction.
Essentially, the total fee is a simple multiplication problem: the amount of gas your transaction actually uses is multiplied by the price you pay for each unit of gas (which is the base fee plus your tip).
The formula is straightforward: Total Fee = Gas Units Used × (Base Fee + Priority Fee). This calculation is the engine driving every single crypto gas fee payment on the network.
How Crypto Gas Fees Are Calculated

To really get a handle on crypto gas fees, you need to peek under the hood at how they're actually calculated. It's not just a random number; there's a specific formula at work, especially on networks like Ethereum after its major EIP-1559 upgrade.
The basic math looks like this:
Total Fee = Gas Limit × (Base Fee + Priority Fee)
Let’s break down what each of those pieces means. We’ll use a common business scenario—an online store processing a customer's crypto payment—to see how this plays out in the real world.
Gas Limit: The Fuel Tank
First up is the Gas Limit. The easiest way to think about this is like deciding how much fuel you're willing to put in your car for a specific trip. You’re setting the maximum amount of computational effort (gas) your transaction is allowed to use.
A simple crypto transfer is like a quick drive across town—it doesn't need much gas, so the limit is usually a standard 21,000 units. A more complex operation, like running a smart contract for an NFT sale, is a cross-country road trip and needs a much higher limit.
The great thing about the gas limit is that it acts as a safety net. It prevents a bug or error in a smart contract from accidentally burning through all the crypto in your wallet. If the transaction ends up using less gas than the limit you set, the leftover amount is simply returned to you.
Base Fee: The Standard Toll
Next, we have the Base Fee. This is like the standard toll you have to pay to get on the blockchain highway. It's not set by you or the person you're paying; it's determined automatically by the network itself based on how busy it is.
Think of it as surge pricing on a ride-sharing app. When everyone is trying to get a ride at the same time, prices go up. Similarly, when the blockchain is congested with lots of transactions, the base fee rises to manage the demand. When things quiet down, it drops.
An interesting detail is that this base fee is actually "burned"—it gets removed from circulation permanently instead of going to the validators. This process helps to slightly reduce the overall supply of the cryptocurrency.
Priority Fee: The Express Lane Tip
Finally, there’s the Priority Fee, which most people just call a "tip." This is a little extra you can add on to your transaction to make it more appealing to the validators who are building the next block of transactions.
During busy times, when blocks are filling up fast, a higher tip is like slipping the bouncer a little extra to get into the club. It gives validators an incentive to pick your transaction out of the crowd and process it sooner.
For a business, this is a powerful tool. Adding a small tip can mean the difference between a customer's payment confirming in seconds or getting stuck for minutes. A smooth, fast checkout is always the goal, and underpaying here can lead to a frustrating customer experience. To get this right, you need a good read on current network conditions, which is where a solid gas fee estimator comes in handy. You can see this in action by checking real-time costs with our crypto fee estimator.
The volatility of these fees can be wild. Ethereum's gas costs can be as low as 10 Gwei during off-peak hours but can easily spike to over 200 Gwei when something big is happening in the market. As data from sources like YCharts shows, simply timing your transactions can make a huge difference—sometimes cutting costs by 40-60% just by waiting for a weekend or early morning hours when network traffic is lower.
Understanding Why Gas Fees Suddenly Spike
If you've spent any time in crypto, you've felt the sting of a sudden gas fee spike. One minute, a transaction costs a few dollars; the next, it’s a jaw-dropping fifty. This isn't random chaos. It's the raw, real-time economics of supply and demand playing out on the blockchain.
Think of it like the moment a hyped-up NFT collection goes live. Thousands of people all try to mint at the exact same second, unleashing a tidal wave of transactions. They're all fighting for the same thing: a tiny, finite amount of space in the very next block.
The Bidding War for Block Space
Every block has a strict size limit; it can only hold so many transactions. When the demand to get into that block wildly outpaces the available space, a fierce bidding war erupts.
Users who are desperate to get their transaction through first start offering higher priority fees—basically, a tip—to the validators. This is where things get interesting. Validators are in it to make a profit, so they naturally grab the transactions with the biggest tips first. The network's fee algorithm sees this surge in demand and automatically cranks up the base fee for everyone, sending the overall crypto gas fee through the roof.
And that's your gas spike. It’s a digital traffic jam where everyone starts honking and waving cash to get to the front, forcing the toll price for the entire highway to skyrocket. For a business, this kind of volatility can be crippling.
- Delayed Payments: Customer payments can get stuck in limbo for hours.
- Failed Transactions: During a flash sale, transactions might fail completely if the fee was set too low for the sudden congestion.
- Eroded Profits: Unexpectedly high fees can easily eat up the entire profit margin on smaller sales.
You can watch this happen live using tools like Etherscan's Gas Tracker.
This screenshot gives you a live look at what people are paying. When you see that "High" priority fee in Gwei creeping up, you know a bidding war is on. It's a clear signal to hold off on any non-urgent transactions.
A sudden jump in the gas fee is the blockchain’s emergency flare. It signals intense network demand and is the system's way of managing the congestion, pushing out less critical activity to make way for those willing to pay a premium for speed.
This isn’t just a theory. Back in the NFT craze of 2021, average Ethereum gas fees routinely blew past $50 per transaction. On peak days, people were shelling out hundreds of dollars for a single trade. You can see the brutal reality for yourself by looking at the Ethereum transaction fee history on BitInfoCharts. For merchants, understanding the drivers behind these increased blockchain fees for Ethereum isn't just a good idea—it's critical for survival.
Actionable Strategies to Reduce Gas Fees
Knowing why crypto gas fees can get so wild is one thing, but actually doing something about it is what really matters. The good news is, businesses aren't just at the mercy of the network. There are several concrete strategies you can use to wrestle those transaction costs back under control.
The simplest trick in the book? Timing. It’s a lot like avoiding rush-hour traffic. Blockchain networks like Ethereum operate 24/7, but their traffic definitely has peaks and valleys. If you can process transactions during off-peak hours—say, late at night in North America or over the weekend—you’ll often find the base fees are dramatically lower.
This whole process boils down to supply and demand. When demand for block space outstrips the limited supply, it kicks off a bidding war.
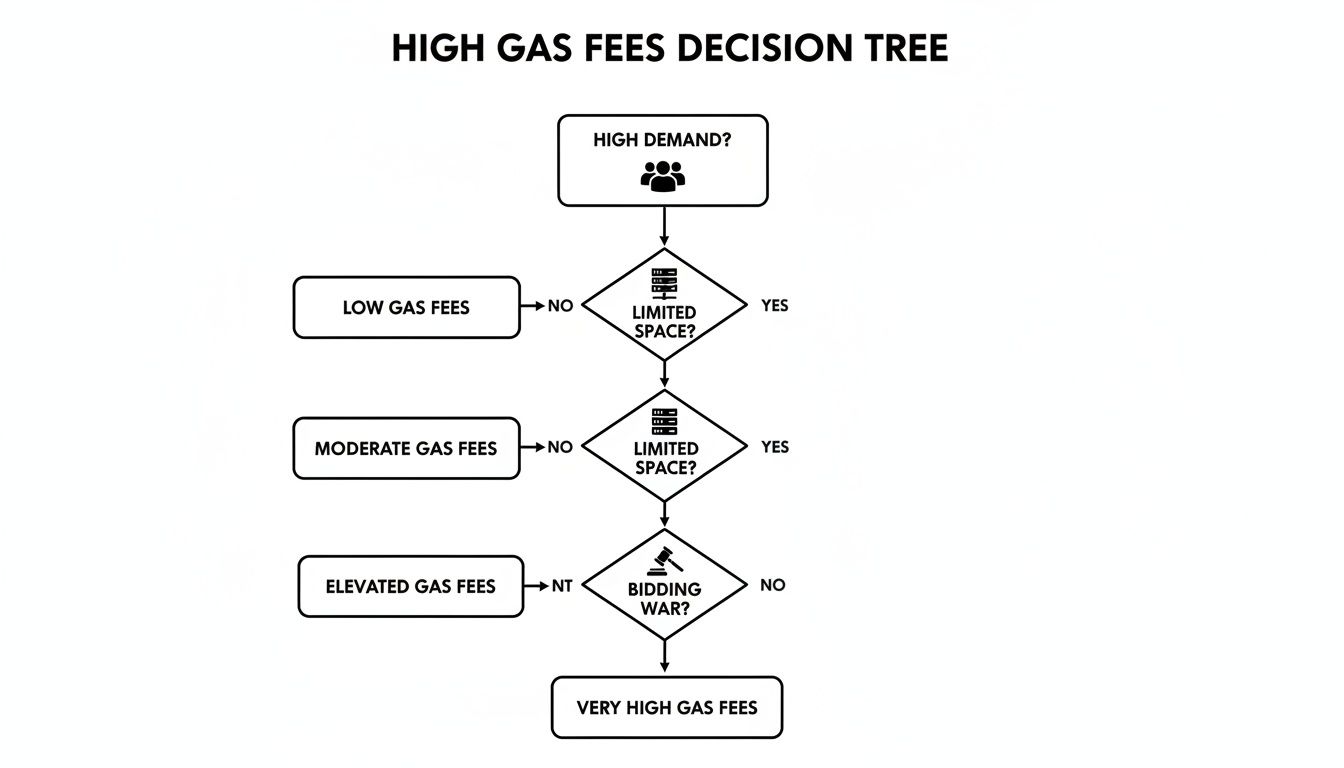
As you can see, when too many people are trying to cram their transactions into the next block, the only way to jump the queue is to offer a bigger tip. This dynamic is what causes those eye-watering fee spikes for everyone.
Move to the Express Lane with Layer-2 Solutions
Of course, waiting for the perfect time isn't always an option, especially if you're running a business that needs to process payments around the clock. That’s exactly where Layer-2 scaling solutions make their entrance.
Think of a Layer-2 network as an express toll road built right alongside the main blockchain highway. Solutions like Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism process transactions on their own speedy, low-cost chains. Then, they cleverly bundle up a huge batch of these transactions and settle them on the main Ethereum network in one go.
For businesses, this approach is a game-changer:
- Drastically Lower Fees: We’re talking pennies. Transaction costs on Layer-2s are just a tiny fraction of what you'd pay on the mainnet during a busy period.
- Faster Confirmations: With less congestion, payments get confirmed almost instantly. That means a much happier customer at checkout.
By building on a Layer-2, you get the security and trust of a major blockchain without directly suffering from its high fees and sluggish speeds.
The Power of Batching and Smart Tools
Another fantastic strategy, particularly for businesses that make a lot of payouts, is transaction batching. Instead of sending 100 separate payments and paying 100 separate gas fees, you can group them all into a single, highly efficient transaction. It’s perfect for running payroll, paying affiliates, or settling up with suppliers. In many cases, this can slash your total gas costs by over 90%.
Batching transactions is just common sense for cost savings. It’s the difference between mailing one hundred individual letters and sending one big parcel—the per-item cost plummets.
Finally, never go into a transaction blind. Using a gas fee estimator is non-negotiable for anyone serious about managing costs. These tools scan the network in real-time and suggest the right base fee and priority fee to get your transaction confirmed without overpaying. It puts you back in the driver’s seat, letting you decide the right balance between speed and cost for every single transaction.
Here's a quick look at how these different techniques stack up.
Gas Fee Reduction Techniques Compared
| Strategy | How It Works | Best For | Potential Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timing Transactions | Processing transactions during off-peak network hours (e.g., weekends, late nights). | Businesses with non-urgent, schedulable transactions. | Impractical for real-time customer payments or urgent needs. |
| Layer-2 Solutions | Moving operations to a faster, cheaper sidechain that settles on the mainnet later. | High-volume businesses, dApps, and customer-facing payments. | Requires integration and moving liquidity to the L2 network. |
| Transaction Batching | Combining multiple outgoing payments (e.g., payroll) into a single transaction. | Businesses making mass payouts. | Not applicable for single, incoming customer payments. |
| Using Gas Estimators | Using real-time tools to set an optimal fee instead of relying on wallet defaults. | All users and businesses for every transaction. | Requires a manual step; market can change quickly after you set the fee. |
By combining these tactics, you can shift from simply reacting to high fees to proactively managing them, turning a major operational headache into a predictable business expense.
How to Mitigate Gas Fee Risk for Your Business
Knowing how gas fees in crypto work is one thing, but as a business, you need practical ways to shield yourself from them. High, unpredictable fees don't just annoy customers; they can eat directly into your profit margins. A smart payment platform is your first line of defense, taking the guesswork and volatility out of the equation so you can focus on running your business.
This is exactly where a tool like BlockBee becomes a game-changer. Instead of being locked into a single, often congested blockchain, you get instant flexibility. By supporting over 70 different cryptocurrencies, BlockBee lets you offer low-fee payment alternatives right at checkout, without any extra work.
What does that mean in practice? You’re no longer a hostage to Ethereum’s notorious rush-hour traffic. You can let your customers pay on more efficient networks, including various Layer-2 solutions, which means faster transactions and much lower costs for everyone. That simple choice can turn a frustrating, expensive checkout into a smooth, easy one.
Streamlining Payouts and Reducing Operational Load
Accepting payments is only half the battle. Sending them out—for payroll, affiliate commissions, or supplier invoices—can be another huge drain on resources thanks to gas fees. If you're processing each of those payments one by one, the costs add up fast. It's just not a scalable approach.
BlockBee’s Mass Payouts feature is built to solve this exact problem. It lets you bundle hundreds, or even thousands, of individual payments into a single, optimized transaction. This batching technique can slash your total gas costs by over 90%, transforming a major operational headache into a minor, manageable expense.
By consolidating multiple transfers, you essentially pay the network fee just once for the entire batch. This simple shift provides enormous savings and makes your accounting way simpler.
On top of that, getting started shouldn't require a whole development team. Solutions like BlockBee are designed for easy adoption, offering a straightforward API and pre-built plugins for major e-commerce platforms like WooCommerce and Magento. This removes the technical burden of having to constantly monitor networks and calculate optimal fees on your own.
Predictability in an Unpredictable Market
Ultimately, the goal is to make accepting crypto as reliable and predictable as using a credit card. A non-custodial platform is key here, as it ensures you always have full control over your funds, with payouts landing directly in your wallet instantly. You're never waiting on a third party to release your money.
By combining multi-chain support, transaction batching, and simple integration, BlockBee provides a complete toolkit for managing the risks of gas fee volatility. It helps you offer a better customer experience while protecting your bottom line from sudden network spikes.
This approach turns a complex technical problem into a simple, solved one, letting you confidently embrace crypto payments. To dive deeper, our detailed guide on gas fees in crypto offers more context on how these mechanics impact your daily operations.
Your Gas Fee Questions, Answered
Alright, even after getting the hang of how gas fees work, you're bound to have some lingering questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that pop up, so you can handle transaction costs like a pro.
Is it Possible for a Crypto Transaction to Have Zero Gas Fees?
For the most part, no. On major networks like Ethereum, every single thing you do—whether it's sending a token or running a complex DeFi protocol—requires validators to do some work. The gas fee is how you pay them for that effort. It’s what keeps the network secure and stops people from spamming it with junk transactions.
That said, you might come across so-called "gasless" transactions. This is a bit of a magic trick; the fee doesn't vanish, it just means someone else is picking up the tab for you.
Here’s how that usually works:
- Sponsored Transactions: A dApp or a wallet might pay your gas fee to make their service more attractive, especially for onboarding new folks.
- Paymaster Services: Some newer services let developers set things up so you can pay your gas fee in a familiar token, like USDC. The service then pays the validator in the required native token (like ETH) behind the scenes.
So, while it might feel free to you, rest assured, someone is always paying the gas fee.
What Happens if I Set My Gas Fee Too Low?
Setting your gas fee too low is a classic rookie mistake, and it almost always ends in frustration. When you send a transaction, you're essentially placing a bid for a spot in the next block. If your bid is way below what everyone else is offering, validators will just skip right over it for higher-paying jobs.
This usually leads to one of two things:
- A Stuck Transaction: Your transaction gets marooned in the "mempool"—basically a digital waiting room. It will just sit there until, by some chance, the network gets quiet and the base fee drops to a level that matches your lowball offer. This could take minutes, hours, or even days.
- A Dropped Transaction: If it's stuck for too long, some network nodes will eventually just give up and drop it from the mempool altogether.
A stuck transaction is a real pain because it often freezes your wallet. You can't send any new transactions from that address until the stuck one is either finally confirmed or you figure out how to cancel it.
The bottom line: Trying to cheap out on gas is a gamble that rarely pays off. You'll likely end up with a stuck transaction, wasting time and energy trying to fix it.
How Do Layer-2 Solutions Actually Lower Gas Fees?
Layer-2 solutions (or L2s) are the real game-changer for tackling high gas fees. They work by taking most of the transaction processing off the main blockchain (Layer-1) and handling it on a separate, much faster layer.
Here's an analogy: Imagine the main Ethereum blockchain is a single, super-busy highway heading into a major city. During rush hour, it gets incredibly congested, and the tolls (gas fees) skyrocket.
A Layer-2 is like building a high-speed rail line that runs parallel to the highway. Thousands of people can hop on the train (process their transactions on the L2), and the train makes just one trip into the city (submits a single, bundled proof to the main blockchain).
Because the L2 bundles thousands of individual transactions into one neat package for the mainnet, the cost of that single mainnet transaction gets split among all the users in that batch. This is how they slash the gas fee in crypto from potentially hundreds of dollars down to just a few cents, making things like micropayments and frequent trading practical again.
Ready to take control of your crypto payments and leave the headache of gas fee volatility behind? With support for over 70 cryptocurrencies, instant payouts, and powerful mass payment tools, BlockBee gives your business the stability and flexibility it needs.
Get started with BlockBee today and see how easy managing crypto can be.
